Ch. 1 Information representation and multimedia
1.1 Data representation
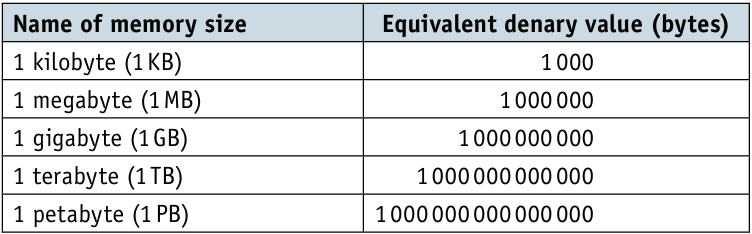
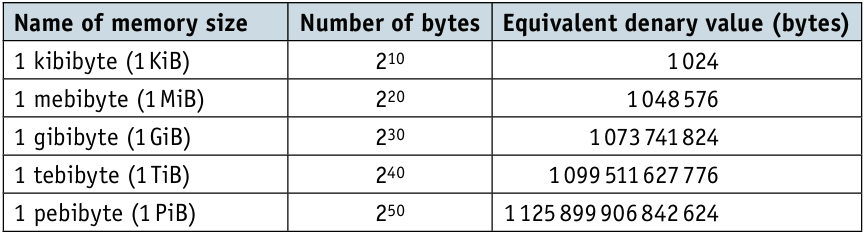
How overflow occurs
- When the value to be stored is larger than the maximum value that can be stored
ASCII, extended ASCII and Unicode
- ASCII
- Limited number of the codes represent non-printing or control characters
- Majority of the codes would be found in an English text
- Includes upper and lower case letters, punctuation marks, denary digits and arithmetic symbols
- Codes are in sequence, if 1 is added to the code for seven, the code for eight is produced
- Codes for upper-case letters differ from the codes for the corresponding lower case letters only in the value of bit 5, which allows a simple conversion
- Unicode
- Able to represent any possible text in code form
- Includes all languages in the world
1.2 Multimedia
How is data for a bitmapped image encoded
- Made up of pixels
- Stored as a two-dimensional matrix of pixels
- Number of bits per pixel is the colour depth/bit depth
Calculation to estimate the file size of an image
- Number of bits × width × height
Effects of changing elements of a bitmap image on the image quality and file size
- If magnified too much, individual pixels will be seen
How data for a vector graphic is encoded
- Property list: stores data about the shapes (black line, font of letter)
- Drawing list: list of shapes involved in an image (triangle, capital letter R)
- Image is scalable
Use of bitmap image or vector graphic
How sound is represented and encoded
- Original analogue sound signal has to be converted to a binary code
- Measured sound values are input to a sound encoder which converts analogue data to digital data
- Sampling resolution is the number of bits used to store amplitude values
- Sampling rate is the number of samples taken per second
Impact of changing the sample rate and resolution
1.3 Compression
Need for compression and examples
Explain lossy and lossless compression and justification of a method in a given situation
- Lossy: file size is reduced with some loss of information and the exact original file could not be recreated
- Lossless: file size is reduced but no information is lost
How a text file, bitmap image, vector graphic and sound file can be compressed
- Lossy
- Reduce number of colours
- Reduce bit depth
- Scale down the image so there are less pixels
- Lossless
- Run-length encoding: compression converts sequences of the same byte value into a code that defines the byte value and the number of times it is repeated