Ch. 15 Hardware
15.1 Processors and parallel processing
RISC and CISC processors
RISC: Reduced instruction set computer
CISC: Complex instruction set computer
RISC processors
- Breaking up the assembly code instructions into a number of simpler single-cycle instructions
- Optimised set of instructions
- Fewer built-in instruction formats
- Higher processor performance
CISC processors
- Based on single complex instructions which need to be converted by the processor into a number of sub-instructions to carry out the required operation
- Makes use of more internal instruction formats
- Carrying out a given task with minimal lines of assembly code
- Hardware must be capable of handling more complex assembly code instructions
| RISC | CISC |
|---|---|
| Fewer instructions | More instructions |
| Simpler instructions | More complex instructions |
| Smaller number of instruction formats | Many instruction formats |
| Single-cycle instructions whenever possible | Multi-cycle instructions |
| Fixed-length instructions | Variable-length instructions |
| Only load and and store instructions to address memory | Many types of instructions to address memory |
| Fewer addressing modes | More addressing modes |
| Multiple register sets | Fewer registers |
| Hard-wired control unit | Microprogrammed control unit |
| Pipelining easier | Pipelining more difficult |
Pipelining
- Perk of RISC
- Allows several instructions to be processed simultaneously without having to wait for previous instructions to be completed
Interrupts
- Once the processor detects the existence of an interrupt, the current program would be temporarily stopped and the status of each register is stored
- The processor can be restored to its original status
Parallel processing
SISD (Single instruction single data stream)
- Uses a single processor
- Handles a single instruction which uses one data source at a time
- Each task is processed in sequential order
- Does not allow for parallel processing
- Found in early personal computers
SIMD (Single instruction multiple data stream)
- Uses many processors
- Each processor executes the same instruction but uses different data inputs
- Doing the same calculations but on different data at the same time
- “Array processors”
- Application in graphic cards
- For example, the brightness of an image made up of 4000 pixels needs to be increased
- Can work on many data items at the same time, so 4000 small processors can each alter the brightness of each pixel by the same amount at the same time
- Application in sound sampling, or any application where a large number of items need to be altered by the same amount
MISD (Multiple instruction single data stream)
- Uses many processors
- Each processor uses different instructions but uses the same shared data source
- Implemented in a fault-tolerant system
- Output would only be accepted if the same output was produced by all the processors
MIMD (Multiple instruction single data stream)
- Similar to SIMD with more than one processing unit receiving the parallel data streams
- The difference is that each processing unit does not execute the same instruction
- Multiple data stream can be provided by a single memory
Parallel computer systems
- The MIMD architecture can be implemented in multicomputer systems known as massively parallel computers
- Used by large organisations for computations involving highly complex mathematical processing
- By linking computers together in this way
- Massively increases the processing power of the single machine
- Each processor will carry out part of the processing
- Communication between computers is achieved via interconnected data pathways
15.2 Boolean algebra and logic circuits
Boolean algebra
| Commutative Laws | A + B = B + A | A.B = B.A |
|---|---|---|
| Associative Laws | A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C | A.(B.C) = (A.B).C |
| Distributive Laws | A.(B + C) = (A.B) + (A.C) (A + B).(A + C) = A + B.C | A + (B.C) = (A + B).(A + C) |
| Idempotent Laws | A.A = A | A + A = A |
| Identity Laws | 1.A = A | 0 + A = A |
| Null Laws | 0.A = 0 | 1 + A = 1 |
| Inverse Laws | A.!A = 0 | A + !A = 1 |
| Absorption Laws | A.(A + B) = A A + (A.B) = A | A + (A.B) = A A + (!A.B) = A + B |
| De Morgan’s Laws | !(A.B) = !A + !B | !(A + B) = !A.!B |
Further logic circuits
- Combination circuit (output depends entirely on the input values)
Two important logic circuits used in computers are
- the half adder circuit
- the full adder circuit
Half adder
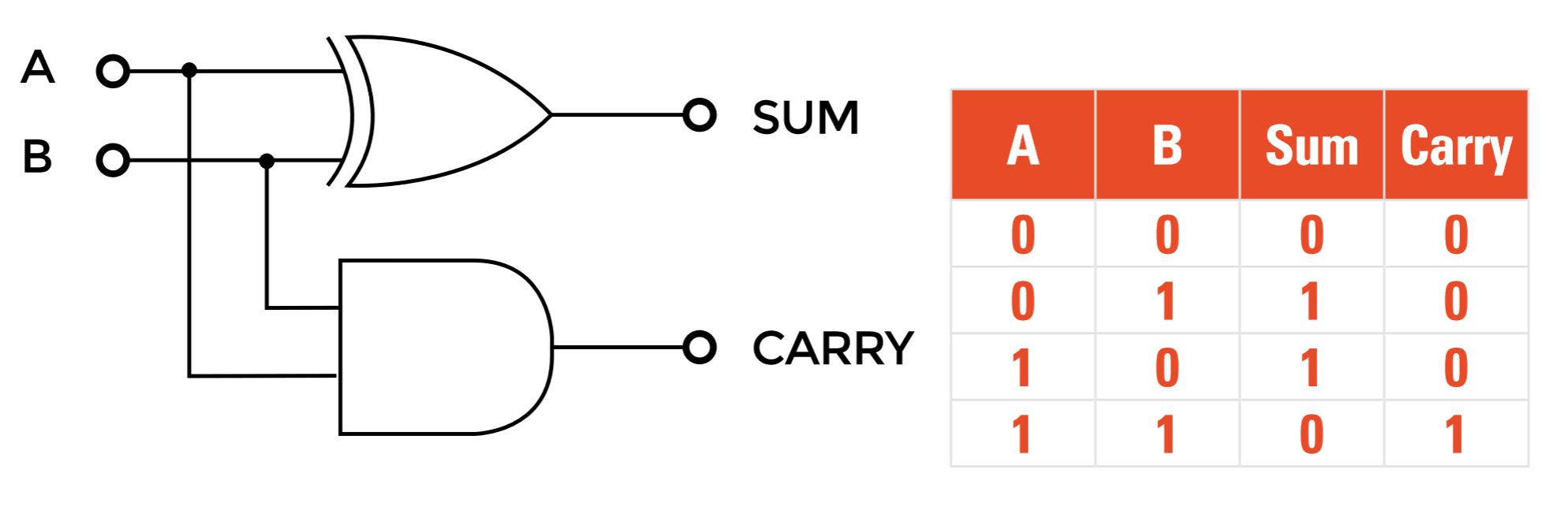
- Simplest circuit
- Carries binary addition on 2 bits generating two outputs
- the sum bit (S)
- the carry bit (C)
- Cannot deal with the addition of several binary bits
Full adder
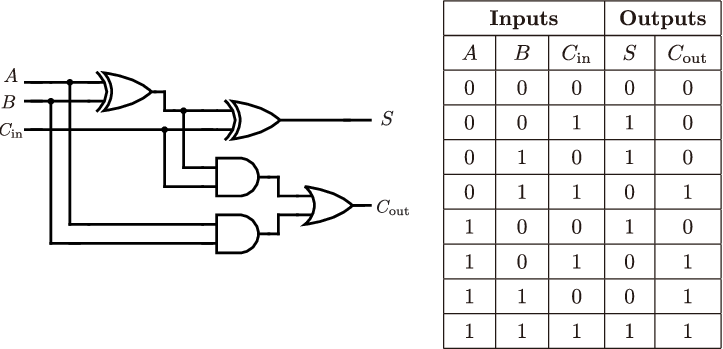
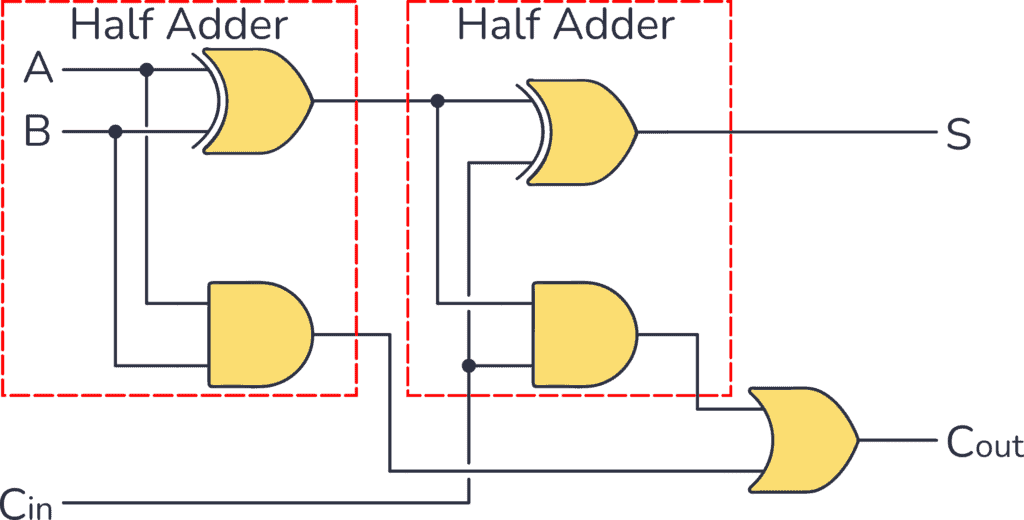
- Formed of two half adders
- To deal with the carry bit
Flip-flop circuits
- Sequential circuit (output depends on the input value produced from a previous output value)
SR flip-flops
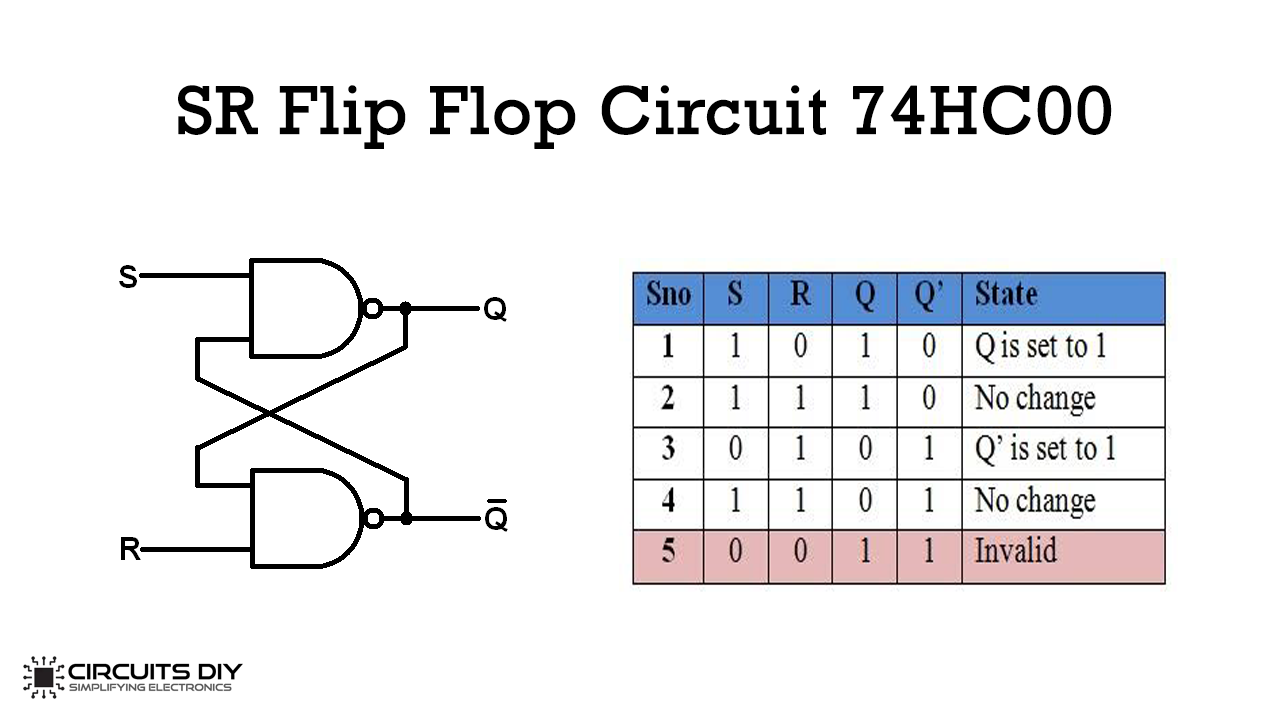
- Consists of two cross-coupled NAND gates
- Can be used as a storage/memory device for one bit
- A value can be remembered but can also be changed
JK flip-flops
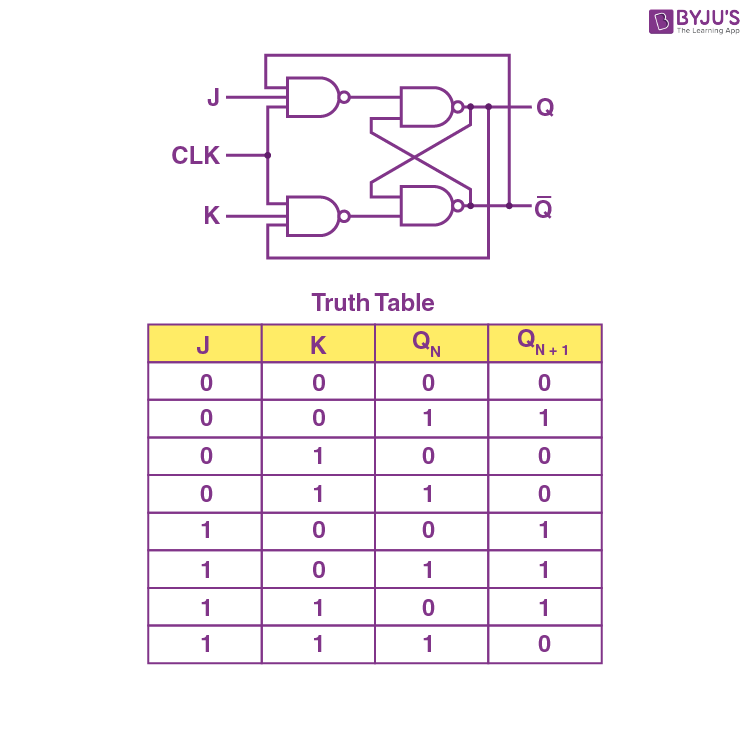
- SR flip-flop problems
- Invalid S, R conditions need to be avoided
- If the inputs do not arrive in time, the flip-flop can become unstable
- Several JK flip-flops can be used to produce shift registers in a computer
- A simple binary counter can be made by linking up several JK flip-flop circuits
Boolean algebra and logic circuits
Karnaugh maps (K-maps)
- The values along the top and the bottom follow Gray code rules
- Only cells containing a 1 are taken account of
- Groups can be a row, a column or a rectangle
- Groups must contain 1, 2, 4, 8, or in general 2^n cells
- Groups should be as large as possible
- Groups may overlap within the above rules
- Single values can be regarded as a group even if they cannot be combined with other values to form a larger group
- The final Boolean expression can only consider those values which remain constant within the group (that is, remain a 1 or 0 throughout the group)