Ch. 8 Databases
8.1 Database concepts
Limitations of using a file-based approach for the storage and retrieval of data
- Storage space is wasted when data items are duplicated by the separate applications; data is redundant
- Data can be altered by one application and not by another; data is inconsistent
- Enquiries available can depend on the structure of the data and the software used; data is not independent
Features of a relational database that address the limitations of a file-based approach
- Storage space is not wasted as data items are only stored once; data is not redundant
- Data altered in one application is available in another application; data is consistent
- Enquiries available are not dependent on the structure of the data and the software used; data is independent
Use of terminology associated with a relational database model
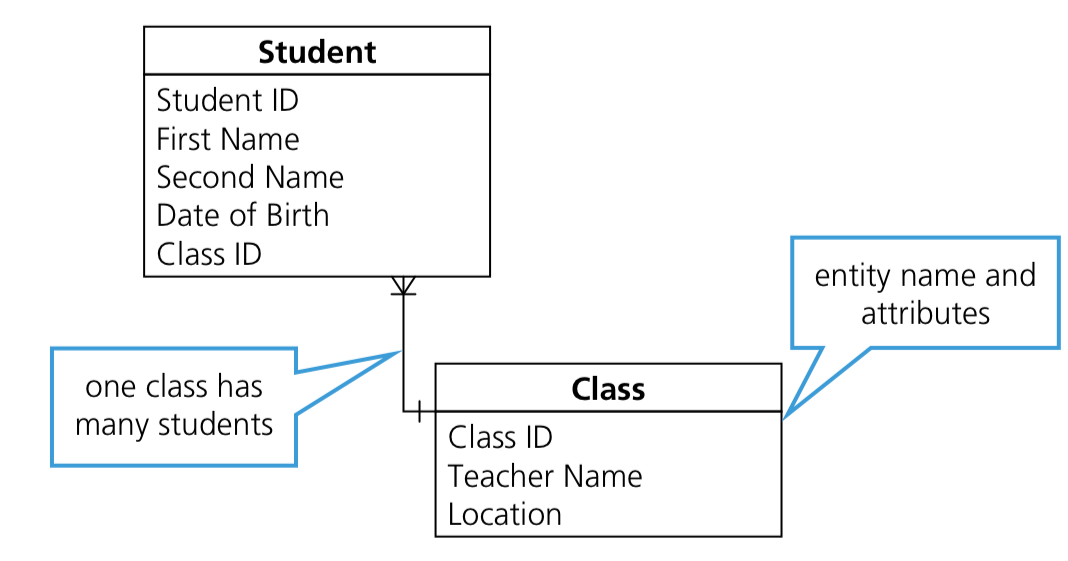
- Entity: anything that data can be stored about, e.g. a student, a teacher
- Table: group of similar data
- Record: a row in a table in a database
- Field: a column/attribute in a table in a database
- Tuple: a row of the table
- Attribute: a column of the table, can be referred to as a field
- Candidate key: an attribute or smallest set of attributes in a table where no tuple has the same value
- Primary key: a unique identifier for a table, a special case of a candidate key
- Secondary key: a candidate key that is an alternative to the primary key
- Foreign key: a set of attributes in one table that refer to the primary key in another table
- Referential integrity: ensures related data in tables are consistent
- Cascading delete
- If a record is deleted in the “primary” table
- all corresponding records in “foreign” tables must also be deleted
- Cascading update
- If a record in the “primary” table is updated
- all linked records in “foreign” tables will also be modified
- Indexing: creating a data structure built from one or more columns in a database table to speed up searching for data
Use an entity-relationship (E-R) diagram to document a database design
Understanding of the normalisation process: 1NF, 2NF and 3NF
- 1NF: entities do not contain repeated groups of attributes
- 2NF: entities are in 1NF and any non-key attributes depend upon the primary key, there are no partial dependencies
- 3NF: entities are in 2NF and all non-key attributes are independent, the table contains no non-key dependencies
Explain why a given set of database tables are, or are not, in 3NF
Produce a normalised database design for a description of a database, a given set of data or a given set of tables
8.2 Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Understanding of the features provided by a Database Management System (DBMS) that address the issues of a file based approach
- data management (data library)
- data library is used to store metadata about the database
- field/attribute names
- table name
- validation rules
- data types
- primary keys//foreign keys
- relationships
- data library is used to store metadata about the database
- data modelling
- shows the data structure of a database, for example, an E-R diagram
- logical schema
- basic relational database data design, made up of the table designs and many relationships
- data integrity
- a DBMS uses a data dictionary to store the metadata, including the definition of tables, attributes, relationships between tables and any indexing
- it can also define the validation rules used for the entry of data and contain data about the physical storage of the data
- used of a data dictionary improves the integrity of the data stored
- data security, including backup procedures and the use of access rights to individuals/groups of users
How software tools found within a DBMS are used in practice, including the use and purpose of:
- developer interface
- allows a developer to write queries in structured query language (SQL)
- query processor
- takes a query written in SQL and processes it
- includes a DDL interpreter, DML compiler and a query evaluation engine
8.3 Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Show understanding that the DBMS carries out all creation/modification of the database structure using its Data Definition Language (DDL)
Show understanding that the DBMS carries out all queries and maintenance of data using its DML
Show understanding that the industry standard for both DDL and DML is Structured Query Language (SQL)
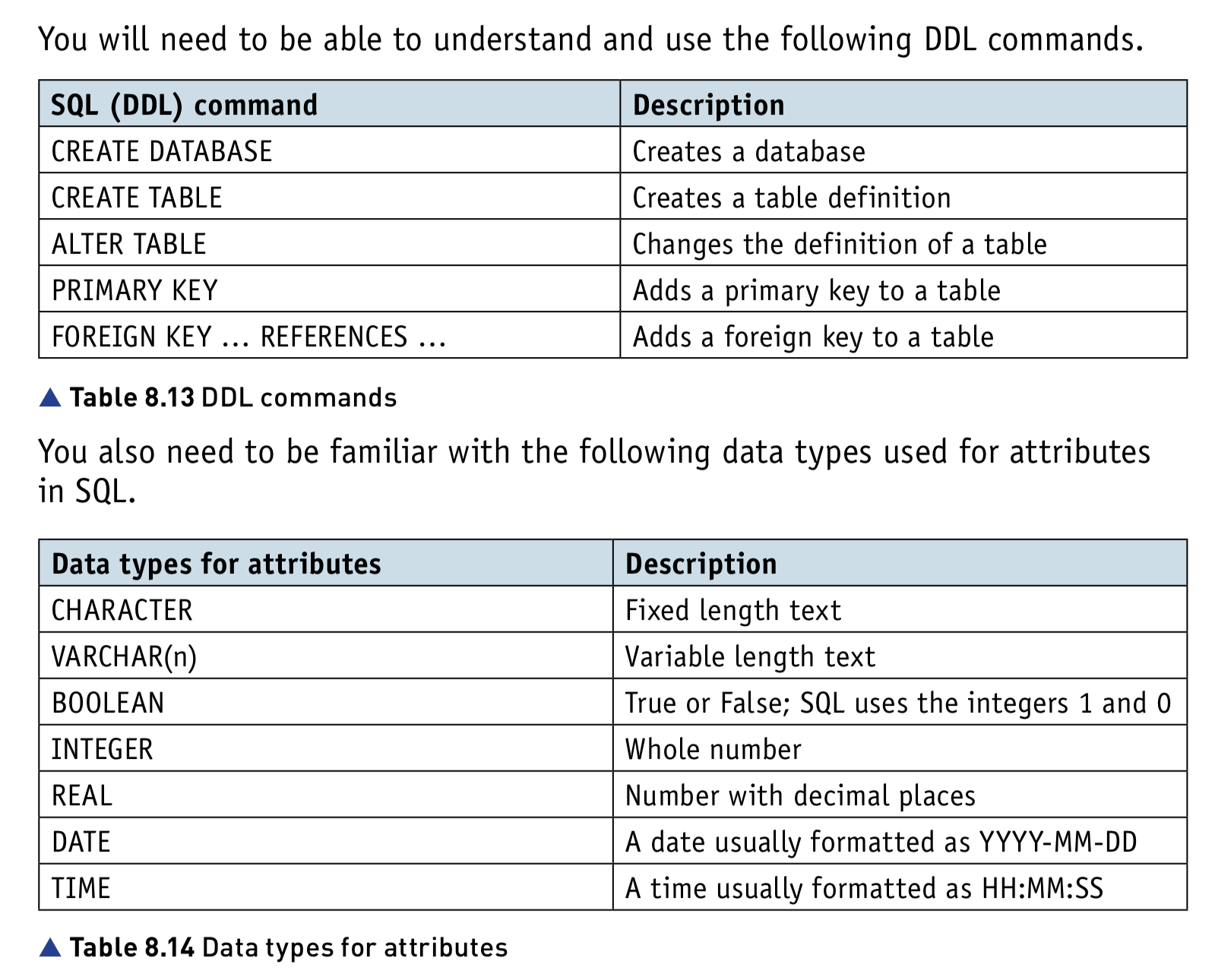
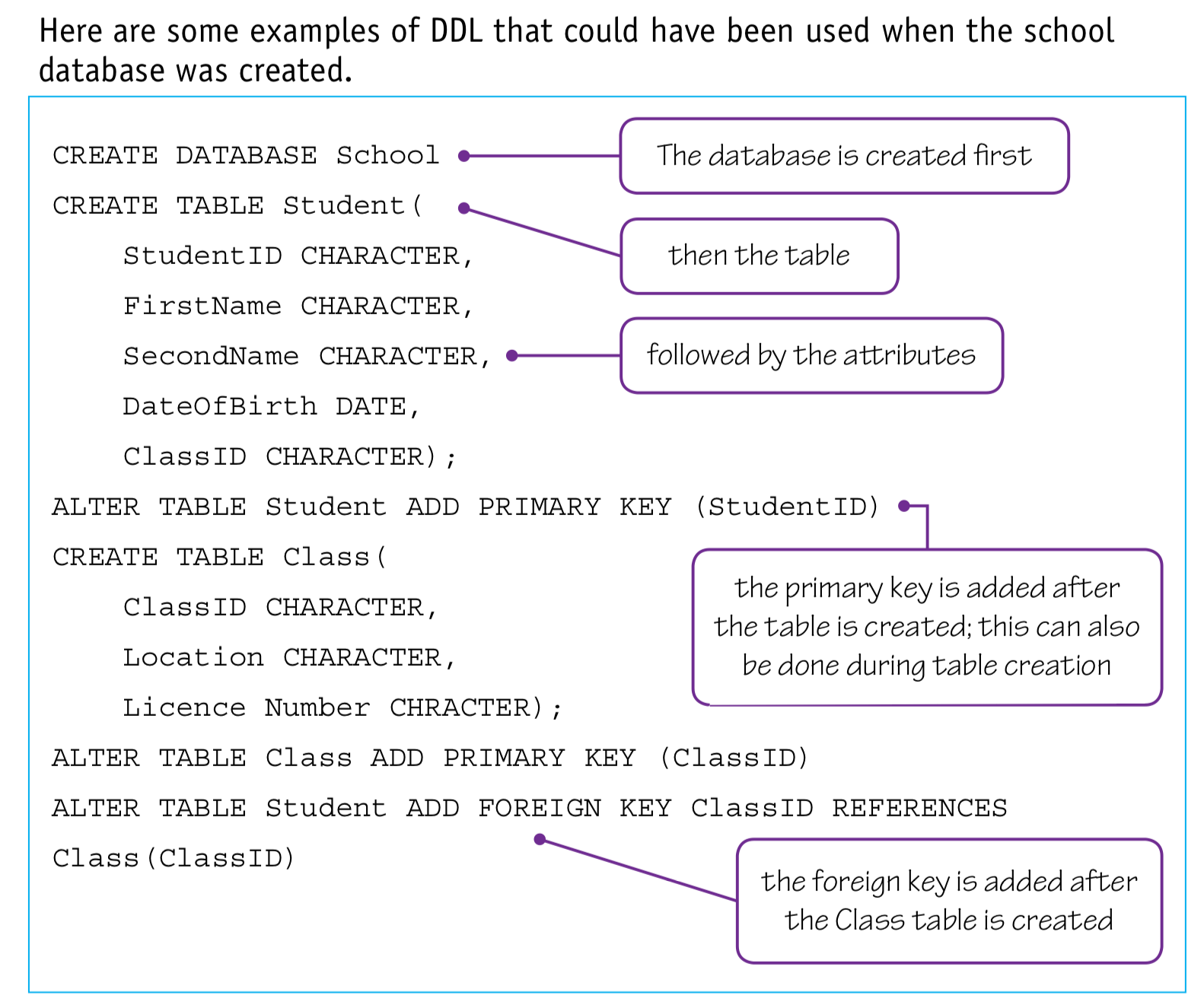
Understand given SQL DDL statements and be able to write simple SQL (DDL) statements using a sub-set of statements
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE TABLE
- CHARACTER
- VARCHAR(n)
- BOOLEAN
- INTEGER
- REAL
- DATE
- TIME
- (ALTER TABLE)
- (PRIMARY KEY (field))
- (FOREIGN KEY (field) REFERENCES Table (field))
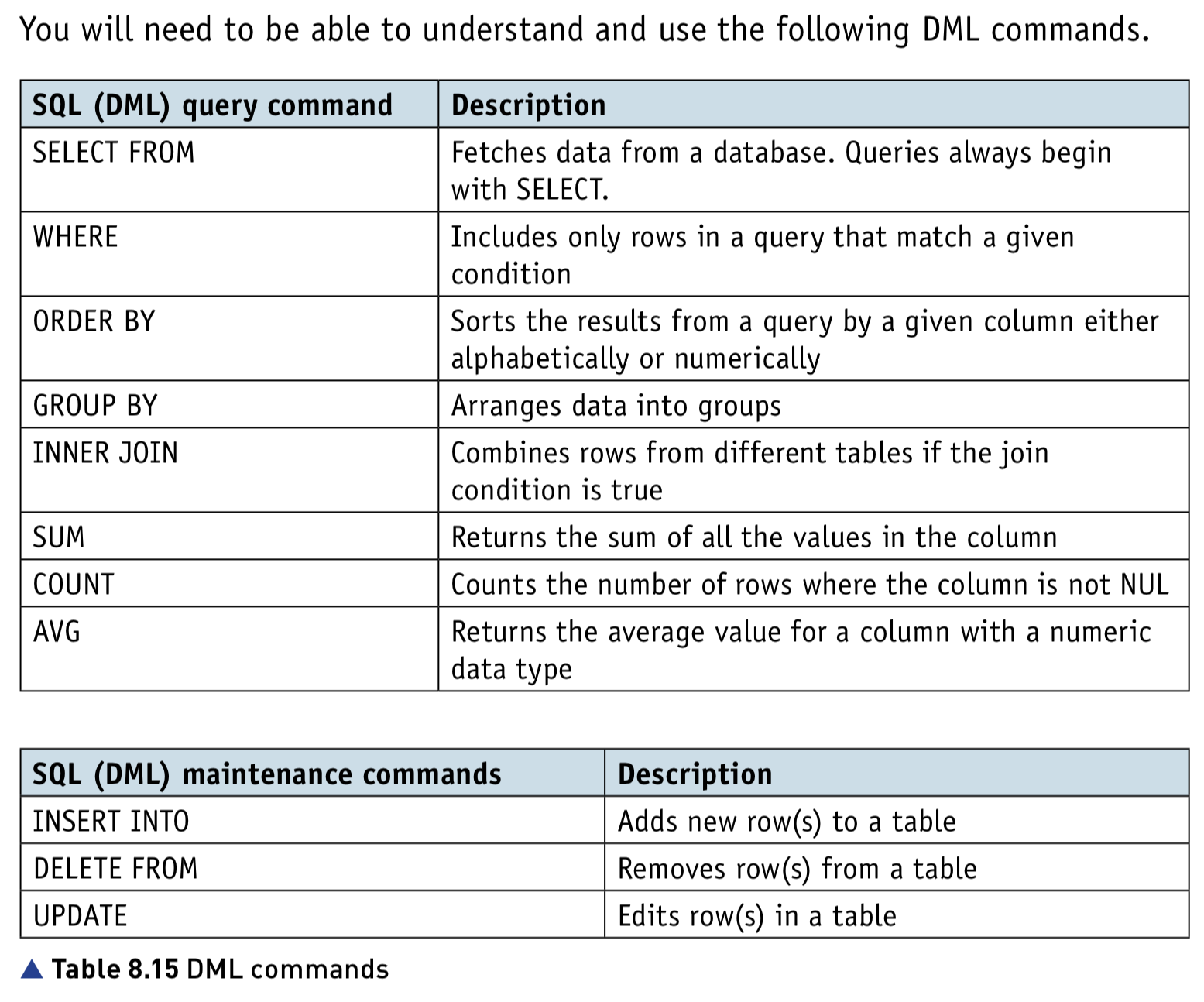
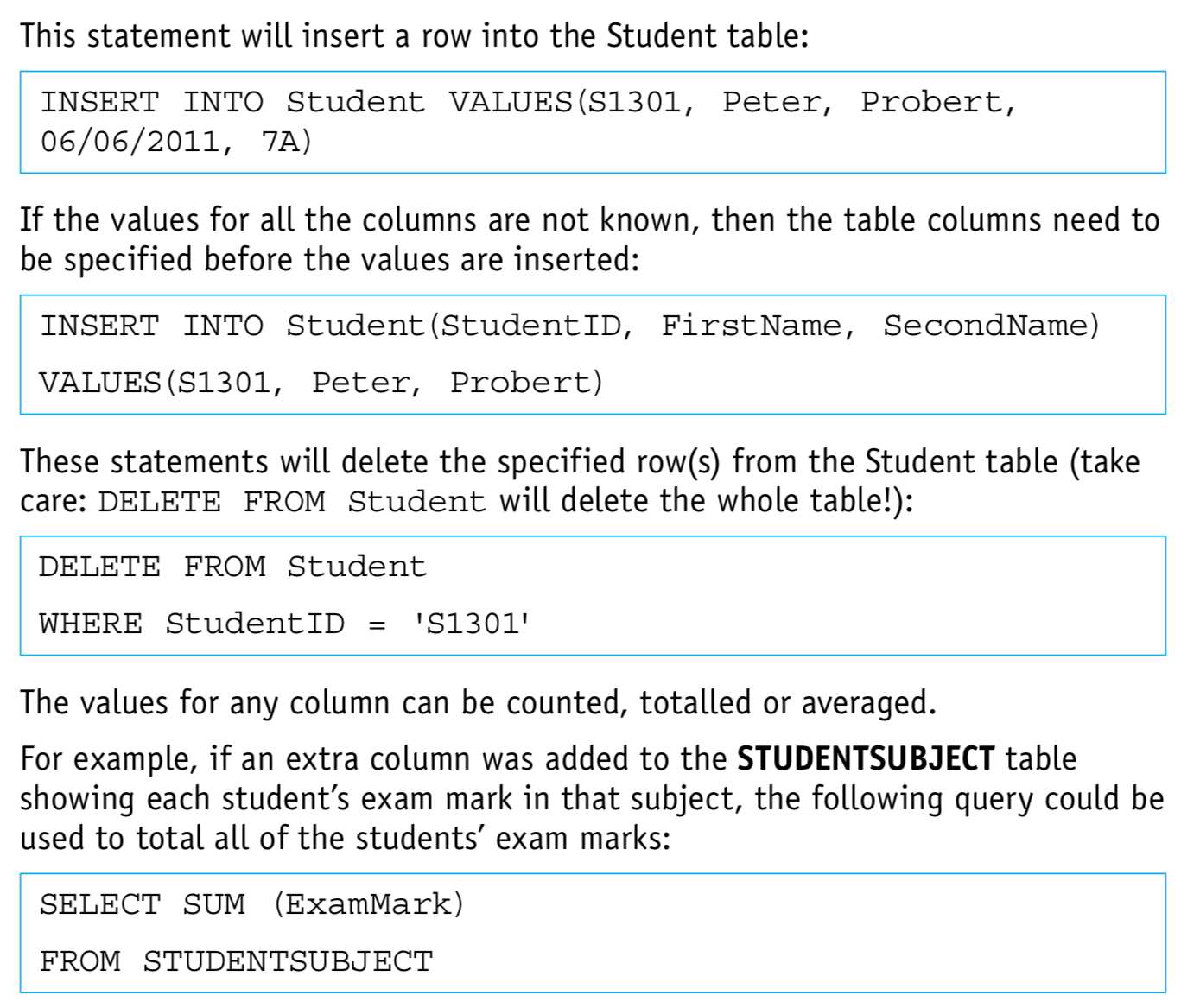
Write an SQL script to query or modify data (DML) which are stored in (at most two) database tables
- Queries:
- SELECT… FROM
- WHERE
- ORDER BY
- GROUP BY
- INNER JOIN
- SUM
- COUNT
- AVG
- Data maintenance:
- INSERT INTO
- DELETE FROM
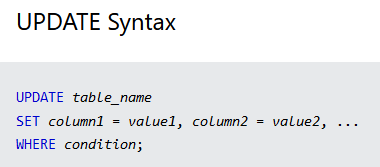
- UPDATE